Dmax
-
The largest displacement between successive presentations for which observers still obtain a coherent sense of motion. For larger steps the displaced object seems to disappear and then reappear at a different location. Increases with retinal eccentricity and is a function of the spatial frequencies in the image. Note that apparent motion can occur at distance much larger than Dmax.
Dark Current
-
Dark Adaptation
-
Dark Light
- Rods spontaneously produce a signal that is indistinguishable from a photon elicited event even in complete darkness about once every 160 msec.
Degree of Convergence
- T
he angle of inclination of the two eyes used in depth perception
Delayed Match-to-Sample
-
Subject is shown a stimulus and then after a delay is required to choose the same stimulus from a number of stimuli to obtain reward
Depth Capture
-
Objects in an image with no apparent depth information can be captured
by surrounding surfaces which do contain depth information.
Depth Cues
-
(See also Monocular Depth Cues).
Diaplopia
-
Double vision.
Dichoptic Stimulation
-
When different images are presented to each eye.
(See also Binoptic Stimulation and Monoptic Stimulation).
Dichromatic Color Vision
-
Color vision based on two cone photoreceptor pigments in the retina.
(See also Trichromatic Color Vision
and Tetrachromatic Color Vision).
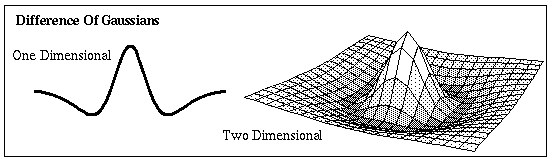
Difference of Gaussians
-
One Dimensional:
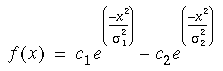
-
Two Dimensional:
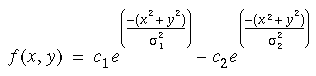
-
Where the constants c1 and c2 control the height of the individual gaussians and the constants
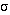 1 and
1 and 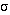 2 control their standard deviations. Generally the inhibitory gaussian (the subtracted term) is chosen with a smaller magnitude and larger standard deviation than the excitatory gaussian (the additive term).
2 control their standard deviations. Generally the inhibitory gaussian (the subtracted term) is chosen with a smaller magnitude and larger standard deviation than the excitatory gaussian (the additive term).
Diffraction
-
The scattering of rays of light by collision with particles of matter as they pass through a medium such as air or water, or pass by a edge or narrow aperture. Plays a role when the pupil is small.
Diopter
-
A diopter is a reciprocal meter. It is a measure of the power of a
lens or optical system in bringing rays to a focus. The dioptric
power of a thin lens is the reciprocal of the distance between the
center of the lens and its focal point as measured in meters.
(See also Optical Power).
Direction Selectivity
-
A difference in the response of a cell to a pattern of light moving through it receptive field according to the direction of movement. Cells respond well when a stimulus moves in one direction and not in the opposite direction.
Discounting the Illuminant
-
Illumination of the visual world tens to be non-uniform, and fluctuates. in order for the visual system to create a consistent perception of color and lightness it must somehow discount fluctuation and gradient in the lighting source.
Discrete Cosine Transform
-
A multiresolution image coding technique used in JPEG. DCT features are products of harmonic functions
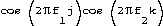 where j and k refer to postion along the hrizontal and vertical directions. Generates a series of transfrom coefficient corresonding to the DCT features in the image.
(See also JPEG).
where j and k refer to postion along the hrizontal and vertical directions. Generates a series of transfrom coefficient corresonding to the DCT features in the image.
(See also JPEG).
Disparity Gradient
-
The ratio of the difference between two feature's disparities and their cyclopean separation. Steeply slanted surfaces have large disparity gradients. Human binocular fusion will only tolerate a disparity gradient of about 1.
Doctrine of Isomorphism
-
(See Gestalt Psychologists).
Dorsal Pathway
-
One of two theorized systems of visual information processing. Information thought to progress toward the parietal cortex V1-> V2 -> MT -> MST -> STP. Functions in comprehension of spatial arrangement.
(See also Ventral Pathway).